











HEED® Sports Drink
- Sustained energy, no sugar crash
- Reduces cramps
- Buffers lactic acid
- Supports dental health
- Cherry Bomb flavor Contains 25mg of Caffeine
2.0 = Tapioca, Classic = Corn






All other “sports drinks” are the same—lots of sugar, salt, and citric acid. Not HEED! The Non-Acidic, subtle-flavored alternative— Packed with complex carbohydrates, complete electrolyte profile, and essential nutrients that balance blood sugar, buffer lactic acid, and ensure long-lasting energy.
Contains xylitol. Do not feed to your dog.
Classic HEED - The original fan favorite, corn based formula introduced in 2004.
2.0 HEED - Updated with tapioca maltodextrin derived from cassava, a far superior energy source, and it’s Paleo friendly.
- What is Hammer Nutrition’s response to the recent headlines about xylitol?
- Why did you switch to a tapioca-derived maltodextrin for HEED 2.0?
- When would I use HEED or Perpetuem?
- Should I use Hammer Gel or HEED?
- What’s the difference between HEED and Endurolytes or Endurolytes Fizz?
- How much HEED do I need per hour?
- Is HEED like Gatorade?
- How do I determine the equivalent of one scoop of HEED?
- Are there any concerns with pre-mixing HEED?
- I noticed that the flavor is very light
- Can Perpetuem and HEED be used in a hydration pack's bladder?
- What is taurine and what is its purpose in Cherry Bomb HEED?
- Is HEED safe for young athletes?
- Do any of the flavors of HEED contain caffeine?
- Why do you use maltodextrin instead of sugar in your fuels?
- Is taurine a stimulant?
- Does Heed contain any diary product, and is it gluten-free?
- Which version of HEED, Perpetuem, and Recoverite are Kosher certified?
- Can a pregnant woman take HEED?
- What is the osmolality of HEED?
- How much manganese in Hammer fuels?
- Is it okay for my dog to consume HEED?
- Is there a recipe for a soy-free Perpetuem?
- How can I prevent any clumping from happening when mixing my fuel bottles?
- Why did the sodium content increase in HEED?
- Why did the scoop size go from 60cc to 43cc?
DON’T BELIEVE THE PROPAGANDA AND THE HYPE!
Q: What is Hammer Nutrition’s response to the recent headlines about xylitol and its supposed negative effects on cardiovascular health?
A: There have been a LOT of headlines lately on xylitol, but we find that they are ALL overly sensationalistic and do not consider much of the actual xylitol study. These headlines are nothing more than scare tactics, and they do a disservice to people looking for reliable and legitimate information.
OUR POSITION: This study, just as is the case with the erythritol study, can show only an association between xylitol and heart risk, a v‑e‑r‑y weak one. It absolutely does not show that xylitol caused or causes a higher incidence of heart attack, stroke, or death.
The information provided below and other variables not accounted for in the study, would make this research more reliable. Dr. F. Perry Wilson said this about the erythritol study—performed by the same research team that did this xylitol study—and we believe it applies here as well: “We shouldn’t be thinking about the results of the study in a vacuum. Even if erythritol does truly increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes, it still is replacing sugar, which almost certainly has more pernicious health effects.”
Here are some of the “red flags” and flaws in the xylitol study:
- As xylitol is found in several fruits and some vegetables and is naturally produced by the body, calling it an artificial sweetener, as some “scientists” do, is incorrect.
- In the study, the investigators measured the level of naturally occurring xylitol in the blood of more than 3,000 participants after overnight fasting. They found that people whose xylitol levels put them in the top 25% of the study group had approximately double the risk for heart attack, stroke, or death over the next three years compared to people in the bottom quarter. This is all based on ONE collection of blood and its xylitol content.
- Xylitol content in the blood, but not xylitol intake via the diet, was considered. No history of the participants’ dietary practices before the study or in the 3-year follow-up period was mentioned in the research. Dr. Leonardo Sodre writes, “At no point did the study's author evaluate the consumption of xylitol, but rather the presence of this type of molecule in the blood.”
- The majority of the participants—average age 64 years old—were very sick to begin with. Many were overweight, had diabetes, hypertension, a history of cardiovascular disease, heart attack, coronary heart disease, stenosis (“the narrowing or restriction of a blood vessel or valve that reduces blood flow), and heart failure. Many were also taking statin medications, which, according to the American Heart Association: “lower cardiovascular event risk, yet paradoxically increase coronary artery calcification, a marker consistently associated with increased cardiovascular risks.”
- The study of naturally occurring xylitol in people’s blood was observational and can show only an association between xylitol and heart risk. It does NOT show that xylitol CAUSED a higher incidence of heart attack, stroke, or death. According to one site, “Observational studies are a lower standard of evidence than experimental studies, are more prone to bias and confounding, and cannot be used to demonstrate causality.” What would seem far more responsible clearly is the participants' health and dietary practices (the latter was not mentioned or recorded in the research).
More information, including charts outlining the participants’ health and other factors, is available upon request at support@hammernutrition.com
Why did you switch to a tapioca-derived maltodextrin for HEED 2.0?
Our carbohydrate-containing fuels used a corn-derived maltodextrin (complex carbohydrate), which was actually a very good maltodextrin. However, we found that tapioca (cassava root)-derived maltodextrin offers the following advantages over corn-derived maltodextrin, which is why we made the switch:
- Tapioca requires far less processing than corn.
- Unlike corn, there is no GMO content in tapioca to begin with, so even though all the corn-derived maltodextrin we used in our products tested at 0ppb for GMOs, going with tapioca just saves us that hassle.
- Tapioca maltodextrin has naturally lower amounts of sodium and higher amounts of naturally occurring potassium. Given that most everyone consumes far too much sodium as it is, having more potassium and less sodium is a definite plus.
- Tapioca maltodextrin has a more-alkaline pH than corn-derived maltodextrin. Considering that we athletes are “acid-producing machines” during exercise, a more-alkaline pH is a highly desirable during-exercise feature/benefit.
- Tapioca maltodextrin has a lower Dextrose Equivalent (DE), which means lower mono and disaccharide (short-chain sugar) content, and a much higher percentage of polysaccharide (complex carb) content--in essence, a more “complex” complex carbohydrate--for even longer-lasting energy and endurance.
- Tapioca maltodextrin has same Glycemic Index (GI) as other forms of maltodextrin, so you get the fast-acting energy that you’re looking for.
When would I use HEED or Perpetuem?
HEED is a “carbohydrate only” drink mix that is great for bouts of exercise up to 2-3 hours in duration. Perpetuem is a “carb + protein + healthy fat” drink mix that is ideal for longer-duration workouts and races. The inclusion of protein in Perpetuem helps to satisfy the 10-15% of energy that must come from protein/amino acids during long-duration exercise. Without this protein donation the body is forced to cannibalize its lean muscle tissue to satisfy this small percentage of energy requirements. That decreases exercise performance, due to the excess amount of fatigue-causing ammonia that is produced, and it will also cause recovery after exercise to be significantly longer because there is a greater percentage of broken down muscle tissue that needs repairing. The healthy fat added to the Perpetuem formula gives the body a cue of sorts to let it know that it’s not depriving it of fat (the “you have to eat fat to burn fat” train of thought). As a result, the body releases its fatty acid stores more liberally so that the calories from them can be used to create energy more consistently and efficiently. As you can see, Perpetuem is a very complete “meal in a bottle” fuel for endurance exercise.
Should I use Hammer Gel or HEED?
Either, it's your preference!
Both products are ideal for use during exercise of any intensity lasting up to 2-3 hours.
Hammer Gel
Hammer Gel is a concentrated complex carbohydrate gel with the consistency of syrup. It is the best choice for athletes who prefer drinking plain water for hydration.
Offered in 12 flavors: Apple-Cinnamon, Banana, Chocolate, Espresso, Montana Huckleberry, Orange, Raspberry, Tropical, Vanilla, Nocciola (Hazelnut-Chocolate), Peanut Butter, and Peanut Butter-Chocolate.
Caffeine Quotient: Espresso contains 50mg and Tropical contains 25mg of caffeine per serving.
HEED
HEED is a powdered sports drink mix. It is the best choice for athletes who DO NOT like drinking plain water while exercising.
HEED comes in five flavors: Cherry Bomb, Lemon-Lime, Orange, Melon, and Strawberry.
Caffeine Quotient: Cherry Bomb contains 25mg of caffeine per serving.
Either product can be used as a partial source of calories during ultra distance events to provide variety and flavor to your primary fuel sources, Perpetuem and/or Sustained Energy.
What’s the difference between HEED and Endurolytes or Endurolytes Fizz?
Every scoop of HEED contains 110 calories and about the same amount of electrolytes as found in one Endurolytes capsule or approximately one-half tablet of Endurolytes Fizz. Neither of these two electrolyte replenishment products are a calories source. Most athletes will fulfill all their calorie needs, as well as at least some of their electrolyte needs for an hour with one to two scoops of HEED in a water bottle. Heavier athletes and/or athletes competing in hot-weather conditions will oftentimes need additional electrolytic mineral support via additional Endurolytes capsules or Endurolytes Fizz tablets.
HEED - Calories + electrolytes
Endurolytes, Endurolytes Fizz - Electrolytes only
How much HEED do I need per hour?
Q: I'm a 200-pound athlete MTB and road cyclist. How much HEED do I need per hour?
A: Most athletes weighing ~200 pounds find that 1.5 to 1.75 scoops of HEED (165 - 192.5 calories) is an excellent amount on a per-hour basis. Also, keep in mind that this will provide the equivalent of 1.5 to about 2 Endurolytes capsules. Athletes in that weight range, and especially in warmer weather, usually need to an additional 2-3 capsules of Endurolytes (up to 4 additional capsules in really hot weather) to fulfill electrolytic mineral needs much more completely.
Is HEED like Gatorade?
The two products are similar in application only... they are during-exercise sports drinks that contain calories and some-to-all electrolytes. Review the labels of both products and you will see some major differences, especially in regards to sugars/added sugars (HEED has no added sugars), artificial ingredients (HEED has none), citric acid (HEED has none), and high amounts of sodium (HEED has significantly less sodium, as well as a full electrolyte profile, while the other product contains only sodium and potassium). HEED also contains auxiliary nutrients to help stabilize blood sugar levels, and to help buffer excess acidity.
How do I determine the equivalent of one scoop of HEED?
No scoop? No problem! With the following conversion information, your "Where did my scoop go?" problems are resolved!
HEED 2.0
1 Level Scoop (39cc) = 2 TBSP +1 ¾ tsp (Serving Size: 1 Scoop)
HEED Classic
1 Level Scoop (60 cc) = 4 TBSP + ½ tsp (Serving Size: 1 Scoop)
Are there any concerns with pre-mixing HEED?
Q: Are there any concerns with pre-mixing HEED with water, say 24-hours in advance?
A: If you premix a bottle of HEED and keep it refrigerated, it will not lose any of its potency or beneficial properties for 24-36 hours. The taste will be somewhat flat and a small amount of the electrolytic minerals and flavoring crystals may have separated and settled to the bottom. If this is the case, simply give the bottle a good shake prior to consumption.
I noticed that the flavor is very light
Q: I being using HEED for about a month already, great results, excellent product. I noticed that the flavor is very light for one scoop in a 24-ounce bottle. Is that normal? Is the light flavor due to the low sugar on the product?
A: The light flavor is by design! When we were in the beginning stages in formulating HEED, the main complaint that we heard from athletes was that all the other sports drinks currently available were too sweet, so that was one major thing we worked on. We always use maltodextrin (complex carbs) in our fuels, and that starch-like carbohydrate is not very sweet to begin with. We wanted to give the product a bit of sweetness, but adding sugar or artificial sweeteners weren't an option. Instead, we opted to use a small amount of xylitol and stevia. Both of these sweeteners are undeniably better options than sugar or artificial ingredients, they’re actually good for teeth and gums, and because they are both several times sweeter than sugar, only a small amount was needed. The result is a sports drink that's not short on calories (110 per scoop), but comes without that unpleasant overly sweet and syrupy taste.
Can Perpetuem and HEED be used in a hydration pack's bladder?
Q: Can Perpetuem and HEED be used in a hydration pack's bladder without clogging it up?
A: While both products can be used in a hydration pack bladder, because Perpetuem is a bit thicker by nature--with its complex carbs, protein, and healthy fat--it has the greater potential to clog. HEED is just an all-carbohydrate fuel, no protein or fat, so it's easier mix in and consume from a hydration pack.
What is taurine and what is its purpose in Cherry Bomb HEED?
Taurine is an amino acid found throughout the body, but especially in muscle and nerve tissue. Taurine assists in regulating heartbeat and muscle contractions, and levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. It is also essential for the proper use of electrolytic minerals—calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium—and ensures proper muscle function. Taurine also increases concentration and focus without stimulating the nervous system. Perhaps most important to athletes, taurine supplementation is correlated with increases in VO2 max and time to exhaustion due to its ability to buffer lactic acid and maintain healthy pH levels.
Is HEED safe for young athletes?
Q: Is HEED safe for young athletes to use during exercise and competitions?
A: HEED is not only 100% safe for young athletes, it's an undeniably a better choice than the plethora of sports drinks available, ones that contain loads of refined sugar and citric acid, as well as artificial sweeteners, flavors, and colors. HEED contains the complex carbohydrate maltodextrin (not refined sugars) and two natural sweeteners - xylitol and stevia - which are not only safe, but also beneficial to teeth and gums.
Do any of the flavors of HEED contain caffeine?
With the exception of the Cherry Bomb flavor (25 mg of caffeine per serving, via the green tea extract), all flavors of HEED are caffeine-free.
Why do you use maltodextrin instead of sugar in your fuels?
Here are the benefits of maltodextrin, along with information about its effects on insulin during exercise and shortly after it’s been completed.
The Benefits of Maltodextrin
- You can digest greater amounts of calories from maltodextrin than from any short-chain sugar, aka “simple sugar,” such as glucose, sucrose, and fructose (As one nutritional scientist states, “maltodextrin allows one to swallow more energy in less volume.”) With maltodextrin you get the full amount of calories that you need for energy production, and with no delay in exiting the GI tract. Fuels containing simple sugars much be mixed at very calorically weak solutions in order to be digested with any efficiency, so your body won’t be getting the right amount of calories it needs. However, when athletes try to make a “double-strength” mix of a simple sugar fuel, that too-high sugar mixture does not match body fluid chemistry, which means it just sits in the stomach undigested for a lengthy period of time... and that means severe stomach distress. You won’t have that issue with maltodextrin.
- Maltodextrin goes to work extremely quickly in producing energy because it’s a high Glycemic Index carbohydrate; in fact, it’s the same as pure glucose (both are 100). That’s a good thing because you want that energy as quickly as possible, and that’s what maltodextrin will do. Another benefit with maltodextrin is that, because it’s comprised of hundreds of saccharide molecules all weakly bonded together, it will provide a much more consistent and longer-lasting energy than glucose or any other simple sugar, and without that undesirable “peak and valley”, “flash and crash” energy that is typical with simple sugars.
Because of maltodextrin’s high Glycemic Index (GI), many people ask about the insulin release that occurs. The answer to that is that, yes, maltodextrin does elevate blood sugar levels very rapidly and will cause an insulin release. This is not an issue immediately prior to exercise, during exercise, however, as Dr. Misner explains: "During exercise, insulin release is inhibited because sympathetic nervous system hormones are also released and, concurrently, exercise augments muscle uptake of glucose from exogenous intake accompanied by lower insulin levels and effects." Basically, what Dr. Misner is saying is that because energy turnover is very high, and with the release of specific central nervous system hormones, the body is able to deliver glucose to the muscles with very minimal insulin… insulin release is not a significant factor during exercise.
After exercise, when the body needs to have its cells restocked with fuel, maltodextrin’s high Glycemic Index is also desirable… Recoverite and Organic Vegan Recoverite are PERFECT fuels for maximizing recovery.
Those are the only three times—immediately prior to exercise, during exercise, and shortly after exercise—when a high-GI carbohydrate such as maltodextrin should be consumed.
Is taurine a stimulant?
Q: I see taurine in all those energy drinks that contain lots of stimulants. Is taurine a stimulant? Is it safe?
A: The amino acid taurine—found in Fully Charged and Cherry Bomb HEED—has gotten a bad rap over the years. The reason? Because it’s an ingredient commonly found in many of the canned energy drinks you can find pretty much anywhere (especially gas stations). These drinks are typically loaded with a variety of unwanted stimulants and excess amounts of caffeine.
Taurine? It kind of “goes along for the ride” in these drinks because of its oftentimes-forgotten effects for helping increase focus, alertness, and concentration. That’s one of the primary reasons it’s in Fully Charged and Cherry Bomb HEED; however, there’s so much more to this oft-maligned amino acid. In fact, the researchers in one study boldly stated, “Considering its broad distribution, its many cytoprotective attributes, and its functional significance in cell development, nutrition, and survival, taurine is undoubtedly one of the most essential substances in the body.” [1] Other researchers refer to taurine as “a wonder molecule.” [2]
General Health
Taurine may very well be one of the most important nutrients to help protect against type II diabetes, with animal research showing that supplementation with taurine supplementation can help reduce the onset of type II diabetes. [3,4]
Studies with diabetic rats have shown that taurine helps support heart function by protecting against heart damage via its ability to increase glucose transport into heart muscle cells, thus lowering blood glucose levels. [5,6]
Taurine has also earned the distinction of being a superb “heart health” nutrient because of its ability to assist in many factors associated with alleviating hypertension. Taurine supplementation helps improve circulation, lower blood pressure, reduce arterial thickening, and enhance the beneficial effects of increased nitric oxide levels. [7, 8, 9]
Taurine is also an outstanding “eye health” nutrient, helping to maintain optimal retinal function [10], and it’s also an extraordinarily beneficial nutrient for liver health. [11, 12, 13]
Athletic performance
Taurine supports enhanced athletic performance by:
- Reducing fatigue [14]
- Increasing VO2max (i.e., the amount of oxygen you can utilize during exercise) [15]
- Increasing muscle and heart contractility, allowing for improved cardiac output and greater exercise workload [16,17]
- Optimizing the proper functioning of electrolytic minerals [18]
- Extending endurance by decreasing the amount of lactic acid/lactate that accumulates [19, 20]
- Lessening muscle tissue breakdown [21]
- Enhancing recovery by providing antioxidant support to protect against free radical damage [15]
Summary
Unlike most other amino acids, taurine is not used to build proteins; however, because it serves many important functions in the body—along with the fact that it’s not readily available in the diet—taurine is classified as a conditionally essential amino acid.
For supporting many aspects of significantly improved athletic performance—with some pretty impressive cross-over benefits for overall health—you’d be hard-pressed to find a more versatile amino acid than taurine.
You’ll find 500 mg of the “wonder molecule” known as taurine in every serving of Fully Charged and in each scoop of Cherry Bomb HEED.
REFERENCES:
[1] Ripps H, Shen W. Review: Taurine: A “very essential” amino acid. Mol Vis. 2012;18:2673-86. Epub Nov 12, 2012.
[2] https://jbiomedsci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S6
[3] Franconi F, Loizzo A, Ghirlanda G, Seghieri G. Taurine supplementation and diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.2006 Jan;9(1):32-6.
[4] Kim KS, Oh da H, Kim JY, et al. Taurine ameliorates hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia by reducing insulin resistance and leptin level in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) rats with long-term diabetes. Exp Mol Med. 2012 Nov 30;44(11):665-73.
[5] Tappia PS, Thliveris J, Xu YJ, Aroutiounova N, Dhalla NS. Effects of amino acid supplementation on myocardial cell damage and cardiac function in diabetes. Exp Clin Cardiol.2011 Fall;16(3):e17-22.
[6] Das J, Vasan V, Sil PC. Taurine exerts hypoglycemic effect in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, improves insulin-mediated glucose transport signaling pathway in heart and ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Jan 15;258(2):296-308.
[7] Murakami S. Taurine and atherosclerosis. Amino Acids.2012 Dec 8.
[8] Abebe W, Mozaffari MS. Role of taurine in the vasculature: an overview of experimental and human studies. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;1(3):293-311.
[9] Rahman MM, Park HM, Kim SJ, et al. Taurine prevents hypertension and increases exercise capacity in rats with fructose-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens.2011 May;24(5):574-81.
[10] Chesney RW. Taurine: its biological role and clinical implications. Adv Pediatr. 1985;32:1-42.
[11] Miyazaki T, Bouscarel B, Ikegami T, Honda A, Matsuzaki Y. The protective effect of taurine against hepatic damage in a model of liver disease and hepatic stellate cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;643:293-303.
[12] Gentile CL, Nivala AM, Gonzales JC, et al. Experimental evidence for therapeutic potential of taurine in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):R1710-22.
[13] Chen X, Sebastian BM, Tang H, et al. Taurine supplementation prevents ethanol-induced decrease in serum adiponectin and reduces hepatic steatosis in rats. Hepatology.2009 May;49(5):1554-62.
[14] Balshaw TG, Bampouras TM, Barry TJ, Sparks SA. The effect of acute taurine ingestion on 3-km running performance in trained middle-distance runners. Amino Acids.2013 Feb;44(2):555-61
[15] Zhang M, Izumi I, Kagamimori S, et al. Role of taurine supplementation to prevent exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy young men. Amino Acids.2004 Mar;26(2):203-7.
[16] Goodman CA, Horvath D, Stathis C, et al. Taurine supplementation increases skeletal muscle force production and protects muscle function during and after high-frequency in vitro stimulation.J Appl Physiol. 2009 Jul;107(1):144-54.
[17] Molaparast-Saless F, Nellis SH, Liedkte AJ. The effects of propionylcarnitine taurine on cardiac performance in aerobic and ischemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Jan;20(1):63-74.
[18] Zhao L, Lou JS, Kang Y. Taurine-magnesium coordination compound attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation induced Ion channel dysfunction in rat ventricular myocytes. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2013 Mar 13. [Epub ahead of print]
[19] Manabe S, Kurroda I, Okada K, et al. Decreased blood levels of lactic acid and urinary excretion of 3-methylhistidine after exercise by chronic taurine treatment in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2003 Dec;49(6):375-80.
[20] Imagawa TF, Hirano I, Utsuki K, et al. Caffeine and taurine enhance endurance performance. Int J Sports Med. 2009 Jul;30(7):485-8.
[21] Dawson R, Jr., Biasetti M, Messina S, Dominy J. The cytoprotective role of taurine in exercise-induced muscle injury. Amino Acids.2002 Jun;22(4):309-24.
Does Heed contain any diary product, and is it gluten-free?
HEED contains no dairy and is 100% gluten-free.
Which version of HEED, Perpetuem, and Recoverite are Kosher certified?
At this time, all flavors of Classic HEED and Classic Recoverite are Kosher certified by the Chicago Rabbinical Council (cRc). We are currently working to obtain Kosher certification for the 2.0 versions of HEED and Recoverite, as well as both Classic and 2.0 versions of Perpetuem.
Can a pregnant woman take HEED?
Q: Can a pregnant woman take HEED for runs, biking, triathlons, etc.?
A: Many of the Hammer Nutrition fuels (such as the non-caffeinated flavors of Hammer Gel) and some of the supplements (such as Premium Insurance Caps and EndurOmega) are generally safe for use during pregnancy. However, before using any supplement or fuel, including HEED, we strongly recommend that you get your doctor's approval first. One reason that this is important is because the maximum safe dose for many nutrients and most herbal supplements for pregnant or nursing women has not been scientifically determined... this would include the amino acids l-carnosine and l-tyrosine in HEED. Another reason to discuss product use with your physician first is because your physician is privy to your medical history to which we have no access. So while it's entirely possible that you may be able to use HEED during pregnancy, it's important that you discuss this product (and share the ingredient list) with your doctor prior to using the product.
What is the osmolality of HEED?
Click here for Osmolality Results.
How much manganese in Hammer fuels?
Q: Why do some of your products contain what seems to be a high amount of manganese, especially when the upper limit for daily intake of manganese is 11 mg.
A: For the most part, the Upper Intake Level (UL)—as it is for other medical/government standards such as the RDA, RDI, and DV—is a standard intended for the general population, and not really applicable for athletes who use/deplete these nutrients at a much higher level than sedentary people do.
When athletes take in nutrients like manganese and the others in an electrolyte product, these nutrients don’t just accumulate, stacking up higher and higher until they reach and exceed UL amounts. Instead, these nutrients—manganese included—are used (and thus, used up) to perform many important bodily functions that occur during exercise. Put another way, when we use a product like Endurolytes Fizz, for example, we are simply resupplying the body with nutrients that it has used up internally to perform the actions they do and/or that are lost in sweat and urine.
Manganese plays an important role as part of the natural antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD), which helps protect against the damage caused by free radicals. Dr. Bill Misner writes, “Manganese is necessary in trace amounts for optimal muscle cell enzyme reactions for the conversion of fatty acids and protein into energy. Researchers suggest that manganese deficiency plays a vital role in glucose tolerance factor (which acts as a physiological enhancer of insulin activity), free radical build-up from intense exercise, and nerve function disorders, especially in older athletes. Endurance exercise increases the rate manganese is lost from the body. Also, please note [there are] three inhibiting minerals—calcium, magnesium, potassium—in both HEED and the Endurolytes products that reduce total absorption rate of manganese.”
Dr. Misner goes on further to state, "You lose (without exercise) an average of 4 mg of manganese from the body each day in the feces (via bile). Typically, when orally dosed, only 3-5% of Manganese is absorbed into the body."
Therefore, because of the role manganese plays in a number of bodily functions during exercise...
- Maximizing muscle cell enzyme reactions for the conversion of fatty acids and protein into energy
- Supporting optimal utilization of insulin
- Protecting against free radical damage via its involvement in the production of SOD
... plus, the fact that absorption rates of orally dosed manganese are extremely minimal, and are also inhibited somewhat by the calcium, magnesium, and potassium components in many of our fuels, we believe that the small amount of manganese we include in them is absolutely merited.
With the Optimum Daily Intake (ODI) of manganese set, as per Dr. Nancy Lieberman, at 15 mg to 50 mg per day, and taking into account that ingested manganese is "used up" during exercise (both for energy-production purposes and antioxidant support), as well as being depleted via sweat and urine, we are convinced that the amounts of manganese we use in our products are not only merited, but extremely beneficial. In fact, highly regarded sports scientist, Dr. Michael Colgan, writes, "Because of their greater bone and soft tissue turnover and their higher metabolism of glucose, athletes may need more manganese than sedentary folk." Now, if someone is sedentary and not exercising, this much manganese is not necessary.
As far as toxicity is concerned, Dr. Lieberman states, "The toxicity for manganese is low when it is ingested in the form of either manganese-rich foods or supplements. Toxicity can occur, however, when manganese is inhaled, as in the case of certain miners who are exposed to high concentrations of manganese oxide in the air." Dr. Michael Colgan elaborates, "Manganese is considered one of the least toxic of the trace elements if taken by mouth."
Our position is that athletes and active people do require a bit more manganese than do sedentary people (though again, Dr. Lieberman's ODI for the general population is set at much higher 15-50 mg/day). With manganese being utilized and thus depleted during exercise for a number of reasons (not simply ingested and stored), we believe that the small amount of manganese in not only merited, but tremendously beneficial.
Hammer Nutrition products containing manganese
- Endurolytes – 0.25 mg per capsule
- Endurolytes Fizz – 3.0 mg per tablet
- Endurolytes Extreme – 1.0 mg per capsule
- Endurolytes Extreme Powder – 0.5 mg per scoop
- HEED – 2.0 mg per scoop
- Recoverite – 2.9 mg per 2-scoop serving
- Organic Vegan Recoverite – 0.6 mg per 2-scoop serving
- Premium Insurance Caps – 1.07 mg per capsule
On a personal note, my (Steve Born) last big thing in my chosen sport of ultramarathon cycling was a record attempt that saw me on my bike for 75.5 hours. I used the original Endurolytes product at a dose of 3-6 capsules per hour, depending on the weather conditions through the Mojave Desert. After successfully completing the record attempt, I calculated that I took in somewhere between 300 and 340 Endurolytes capsules, which means I was intaking 75 – 85 milligrams of manganese. Nothing even close to a toxic response ever occurred, and it was never anything that I was concerned about, the reason being that I knew that I was simply replenishing what my body had used up internally and/or sweated out.
Is it okay for my dog to consume HEED?
No! HEED is not acceptable for consumption by dogs, as it contains xylitol. While xylitol is a superb natural sweetener, and provides numerous beneficial effects on human health, it is highly toxic to dogs. DO NOT give HEED or any food or fuel containing xylitol to your dog!
Is there a recipe for a soy-free Perpetuem?
Q: I cannot consume soy. Is there a recipe for a soy-free Perpetuem?
A: Yes, you can make a non-soy endurance fuel that’s comparable to Perpetuem by using HEED and Vegan Protein:
Each 2-scoop serving of Perpetuem contains 180 calories from 34 grams of carbohydrates, 5 grams of protein, and 2 grams of fat. To make a soy-free version that’s similar to Perpetuem, mix together the following:
- 1.25 scoops of HEED = 137.5 calories from 35 grams of carbohydrates
- 1/3 scoop of Vegan Protein = 40 calories from 2.5 grams of carbohydrates, 6.5 grams of protein, and 0.67 grams of fat
TOTAL CARBOHYDRATES – 37.5 grams
TOTAL PROTEIN – 6.5 grams
TOTAL FAT – .67 grams
TOTAL CALORIES – 177.5
How can I prevent any clumping from happening when mixing my fuel bottles?
Always start with about one-third of your water bottle/blender bottle filled with water. Adding water to dry powder will oftentimes cause clumping, but if you first start with water and then add the powder, this issue will cease to exist. Once you’ve added the powder to the water-containing bottle, put the lid on and shake vigorously. After that, add a bit more water, put the lid on, and repeat the process. Continue until your fuel bottle is full. Note: This is especially important when you’re making a multi-hour bottle of fuel; make it a little bit at a time—add some water, add powder, put the lid on, shake, repeat.
Why did the sodium content increase in HEED?
Q: Why did the sodium content increase in HEED? Did you add more salt to the product?
A: The latest HEED formulation contains 150mg of sodium per serving instead of the original 60mg per serving. We believe that this amount, especially when combined with the balanced blend of the other electrolytic minerals in HEED, will serve more athletes under more conditions. We made sure not to overdo it on the sodium content, however, and 150mg per serving is still a much more reasonable amount as compared to most of the sports drink mixes currently available (including one that has an obscenely high 900mg of sodium per serving).
We did not add more salt (sodium chloride) to the product, but instead added a specific amount of sodium phosphate, a remarkable compound that, among its other benefits, has no peer when it comes to buffering excess acidity (which causes that burning sensation we all hate) while extending endurance by helping maintain optimal blood and muscle pH.
Why did the scoop size go from 60cc to 43cc?
When we added sodium phosphate to the formula, we noted that it is a much denser and heavier ingredient. That’s why the larger, 60cc-sized scoop was no longer required. Instead, we found that the smaller 43cc scoop was the size that worked to ensure that HEED still contains the full number of calories (110/serving) and the same amounts of all of the additional ingredients in the product.
Mix 1 – 1.5 scoops to 12-20 oz. (355 – 591 ml) of water, depending on temperatures. Sip continuously during exercise.
PRO TIP
In hotter climates or during prolonged activities, add one form of Endurolytes® to your HEED.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Xylitol is toxic to dogs and unsafe for their consumption. Do not feed your dog any xylitol-containing products, including HEED or Recoverite, nor any products that are made for human consumption.
2.0 = TAPIOCA Maltodextrin – Less processed, NON-GMO, lower mono and disaccharide content/much higher percentage of polysaccharide content (courtesy of its lower Dextrose Equivalent), less sodium content, and even closer to the desired neutral pH.
Classic = Corn Maltodextrin – A high-glycemic index (GI) complex carbohydrate, ideal for providing fast-acting, long-lasting energy during exercise and for replenishing the body’s energy (glycogen) stores after exercise.
Xylitol – This natural sweetener is found in a variety of fibrous fruits and vegetables. It promotes oral health, as it does not ferment and support the acid-producing bacteria that cause tooth decay. NOTE: It is believed that xylitol is unsafe for consumption by dogs; therefore, we do not recommend you feed your dog any xylitol-containing products, including HEED or Recoverite.
Full-spectrum electrolyte profile – The complete profile of sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, and potassium helps maintain performance of many important bodily functions during exercise, while also helping protect against muscle cramping.
L-Carnosine – One of the most versatile and beneficial nutrients available. It buffers lactic acid during exercise and offers antioxidant support.
Glycine – This amino acid is beneficial for aiding with muscle tissue repair, protecting collagen in joints, and reducing joint pain. Additionally, glycine has a naturally sweet taste, contributing to HEED’s delicious flavor.
L-Tyrosine – Aids in the functioning of the adrenal, pituitary, and thyroid glands, which are responsible for the production and regulation of numerous key hormones. This contributes to increased performance levels and decreased recovery time.
Manganese – This trace mineral is necessary for optimal muscle cell enzyme reactions and for the conversion of fatty acids and protein into energy.
Chromemate® brand chromium polynicotinate – This trace mineral helps regulate blood sugar and plays a vital role in the synthesis of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids.
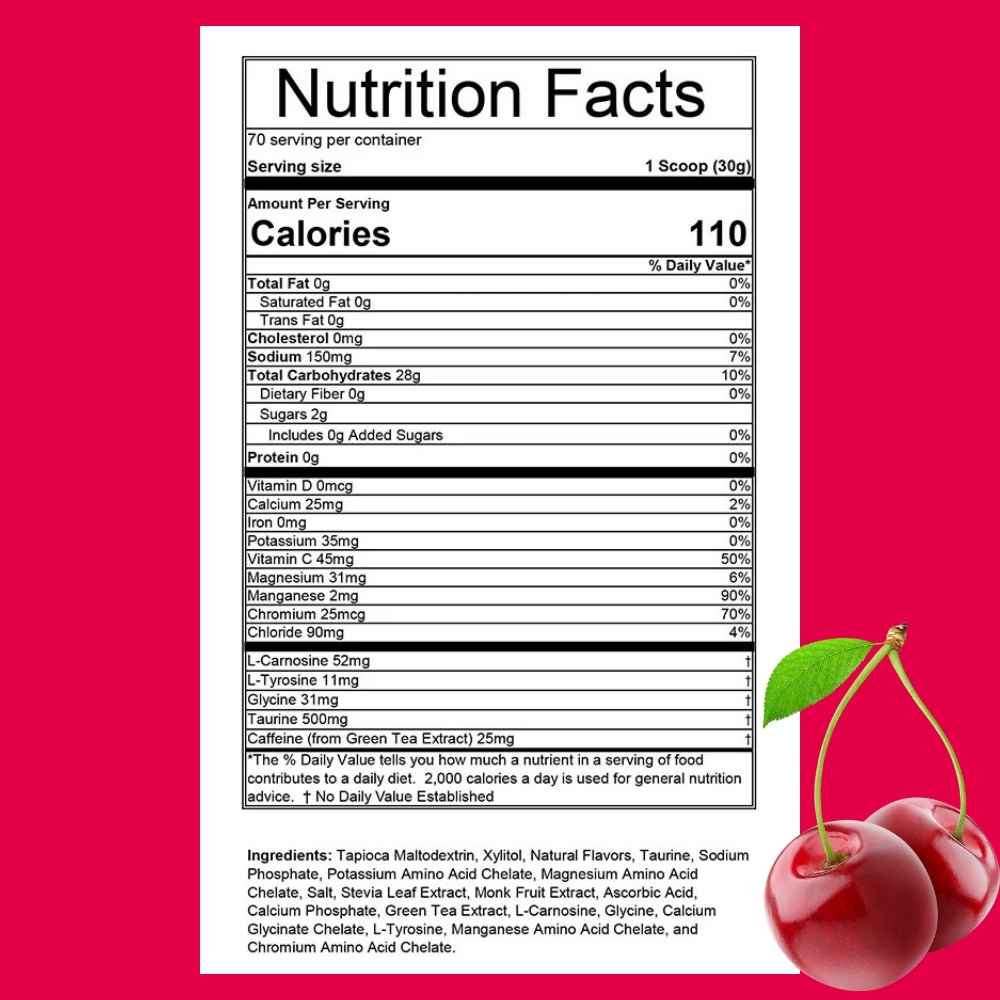
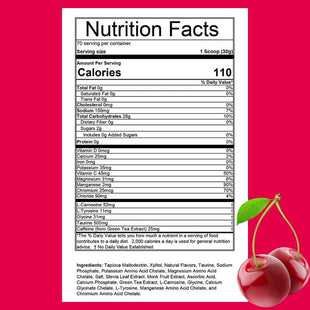
| HEED 2.0 Cherry Bomb Flavor Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 30g (1 Level Scoop or Single Serving Packet) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 28g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 2g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 45mg | 50% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 90% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 70% |
| Chloride | 90mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| Taurine | 500mg | † |
| Caffeine (from green tea extract) | 25mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Tapioca Maltodextrin, Xylitol, Natural Flavors, Taurine, Sodium Phosphate, Potassium Amino Acid Chelate, Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate, Salt, Stevia Leaf Extract, Monk Fruit Extract, Ascorbic Acid, Calcium Phosphate, Green Tea Extract, L-Carnosine, Glycine, Calcium Glycinate Chelate, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, and Chromium Amino Acid Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED 2.0 Lemon-Lime Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 30g (1 Level Scoop or Single Serving Packet) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 28g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 2g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 45mg | 50% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 90% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 70% |
| Chloride | 90mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Tapioca Maltodextrin, Xylitol, Natural Flavors, Sodium Phosphate, Potassium Amino Acid Chelate, Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate, Salt, Stevia Leaf Extract, Monk Fruit Extract, Calcium Phosphate, Ascorbic Acid, L-Carnosine, Glycine, Calcium Glycinate Chelate, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, and Chromium Amino Acid Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED Classic Lemon-Lime Nutrition Facts |
||
| Serving Size: 32g (1 Level Scoop) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 27g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 1g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 57mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 25mg | <1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 9mg | 529% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 87% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 71% |
| Chloride | 91mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Maltodextrin, Natural Flavor, Xylitol, Calcium Chelate, Sodium Phosphate, Magnesium Chelate, Sodium Chloride, Potassium Chelate, Sodium Citrate, Stevia, L-Carnosine, Glycine, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Chelate, Vitamin B6 (as pyridoxine HCl), Chromium Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts, and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED 2.0 Orange Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 30g (1 Level Scoop or Single Serving Packet) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 28g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 2g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 45mg | 50% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 90% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 70% |
| Chloride | 90mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Tapioca Maltodextrin, Xylitol, Natural Flavors, Sodium Phosphate, Potassium Amino Acid Chelate, Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate, Salt, Stevia Leaf Extract, Monk Fruit Extract, Ascorbic Acid, Calcium Phosphate, L-Carnosine, Glycine, Calcium Glycinate Chelate, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, and Chromium Amino Acid Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED 2.0 Melon Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 30g (1 Level Scoop or Single Serving Packet) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 28g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 2g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 45mg | 50% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 90% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 70% |
| Chloride | 90mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Tapioca Maltodextrin, Xylitol, Natural Flavors, Sodium Phosphate, Potassium Amino Acid Chelate, Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate, Natural Color, Salt, Stevia Leaf Extract, Monk Fruit Extract, Calcium Phosphate, Ascorbic Acid, L-Carnosine, Glycine, Calcium Glycinate Chelate, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, and Chromium Amino Acid Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED 2.0 Strawberry Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 30g (1 Level Scoop or Single Serving Packet) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 110 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 28g | 10% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Sugars | 2g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 45mg | 50% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 90% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 70% |
| Chloride | 90mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Tapioca Maltodextrin, Xylitol, Natural Flavors, Sodium Phosphate, Potassium Amino Acid Chelate, Magnesium Amino Acid Chelate, Salt, Stevia Leaf Extract, Monk Fruit Extract, Calcium Phosphate, Ascorbic Acid, L-Carnosine, Glycine, Calcium Glycinate Chelate, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Amino Acid Chelate, Natural Color and Chromium Amino Acid Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. This product contains Xylitol. | ||
| HEED Classic Unflavored Nutrition Facts |
||
|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 28.6g (1 Level Scoop) | ||
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value* | |
| Calories | 100 | |
| Total Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Saturated Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 150mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 26g | 9% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% |
| Total Sugars | 1g | † |
| Added Sugars | 0g | 0% |
| Protein | 0g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 57mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 25mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 9mg | 529% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 87% |
| Chromium | 25mcg | 71% |
| Chloride | 91mg | 4% |
| L-Carnosine | 52mg | † |
| L-Tyrosine | 11mg | † |
| Glycine | 31mg | † |
| * Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Ingredients: Maltodextrin, Calcium Chelate, Magnesium Chelate, Potassium Chelate, Sodium Phosphate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, L-Carnosine, Glycine, L-Tyrosine, Manganese Chelate, Vitamin B6 (as pyrioxine HCl), Chromium Chelate. | ||
| Allergen Warning: Manufactured in a facility that processes Milk, Soy, Eggs, Peanut, Sesame, Shellfish, Tree Nuts and Wheat. | ||



